The DELETE statement is used to delete records in a table.
Create a Database named "Studysql" and a table named "tbl_biodata"
Right click on the database Studysql and select new query.Then we can write queries as per the requirements.
( Click here to know how created this table )
==================================================================================
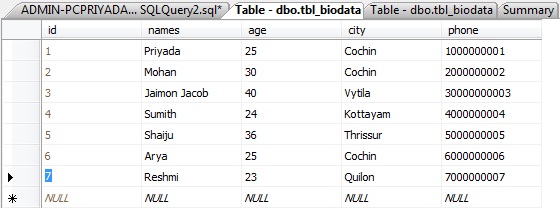
In the previous chapter ( SQL "UPDATE" Statement ) , we inserted a new row "Resmi" as shown :
The created Table is :
Create a Database named "Studysql" and a table named "tbl_biodata"
Right click on the database Studysql and select new query.Then we can write queries as per the requirements.
( Click here to know how created this table )
ID
|
NAME
|
AGE
|
CITY
|
PHONE
|
1
|
Priyada
|
25
|
Cochin
|
1000000001
|
2
|
Mohan
|
30
|
Cochin
|
2000000002
|
3
|
Jaimon Jacob
|
40
|
Vytila
|
3000000003
|
4
|
Sumith
|
24
|
Kottayam
|
4000000004
|
5
|
Shaiju
|
36
|
Thrissur
|
5000000005
|
==================================================================================
In the previous chapter ( SQL "UPDATE" Statement ) , we inserted a new row "Resmi" as shown :

Now , we want to delete the 7th row "Reshmi"
To do so, write the command like this in SQL.
DELETE FROM tbl_biodata WHERE
names ='Reshmi'
AND age='23'
|
When executing we can see ,

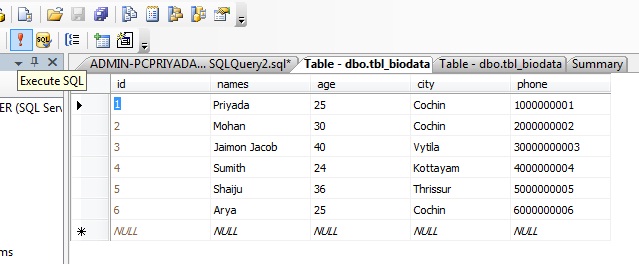
The result-set will look like this:

SQL SELECT Syntax of the above table is :
DELETE FROM table_name
WHERE some_column=some_value
WHERE some_column=some_value
Note: Notice the WHERE clause in the DELETE syntax. The WHERE clause specifies which record or records that should be deleted. If you omit the WHERE clause, all records will be deleted!
It is possible to delete all rows in a table without deleting the table. This means that the table structure, attributes, and indexes will be intact:
DELETE FROM table_name
or
DELETE * FROM table_name
or
DELETE * FROM table_name
Be very careful when deleting records. You cannot undo this statement!
Now , you can move to ADVANCED SQL
No comments:
Post a Comment